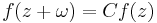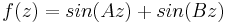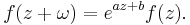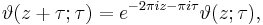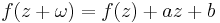Quasiperiodic function
In mathematics, a function is said to be quasiperiodic when it has some similarity to a periodic function but does not meet the strict definition.
A simple case (sometimes called arithmetic quasiperiodic) is if the function obeys the equation:
Another case (sometimes called geometric quasiperiodic) is if the function obeys the equation:
A useful example is the function:
If the ratio A/B is rational, this will have a true period, but if A/B is irrational there is no true period, but a succession of increasingly accurate "almost" periods.
A function with quasiperiod (sometimes simply called the period) ω if for certain constants a and b, f satisfies the functional equation
An example of this is the Jacobi theta function, where
shows that for fixed τ it has quasiperiod τ; it also is periodic with period one. Another example is provided by the Weierstrass sigma function, which is quasiperiodic in two independent quasiperiods, the periods of the corresponding Weierstrass ℘ function.
Functions with an additive functional equation
are also called quasiperiodic. An example of this is the Weierstrass zeta function, where
for a fixed constant η when ω is a period of the corresponding Weierstrass ℘ function.
In the special case where 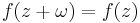 we say f is periodic with period ω.
we say f is periodic with period ω.
Quasiperiodic signals
Quasiperiodic signals in the sense of audio processing are not quasiperiodic functions; instead they have the nature of almost periodic functions and that article should be consulted. The more vague and general notion of quasiperiodicity has even less to do with quasiperiodic functions in the mathematical sense.